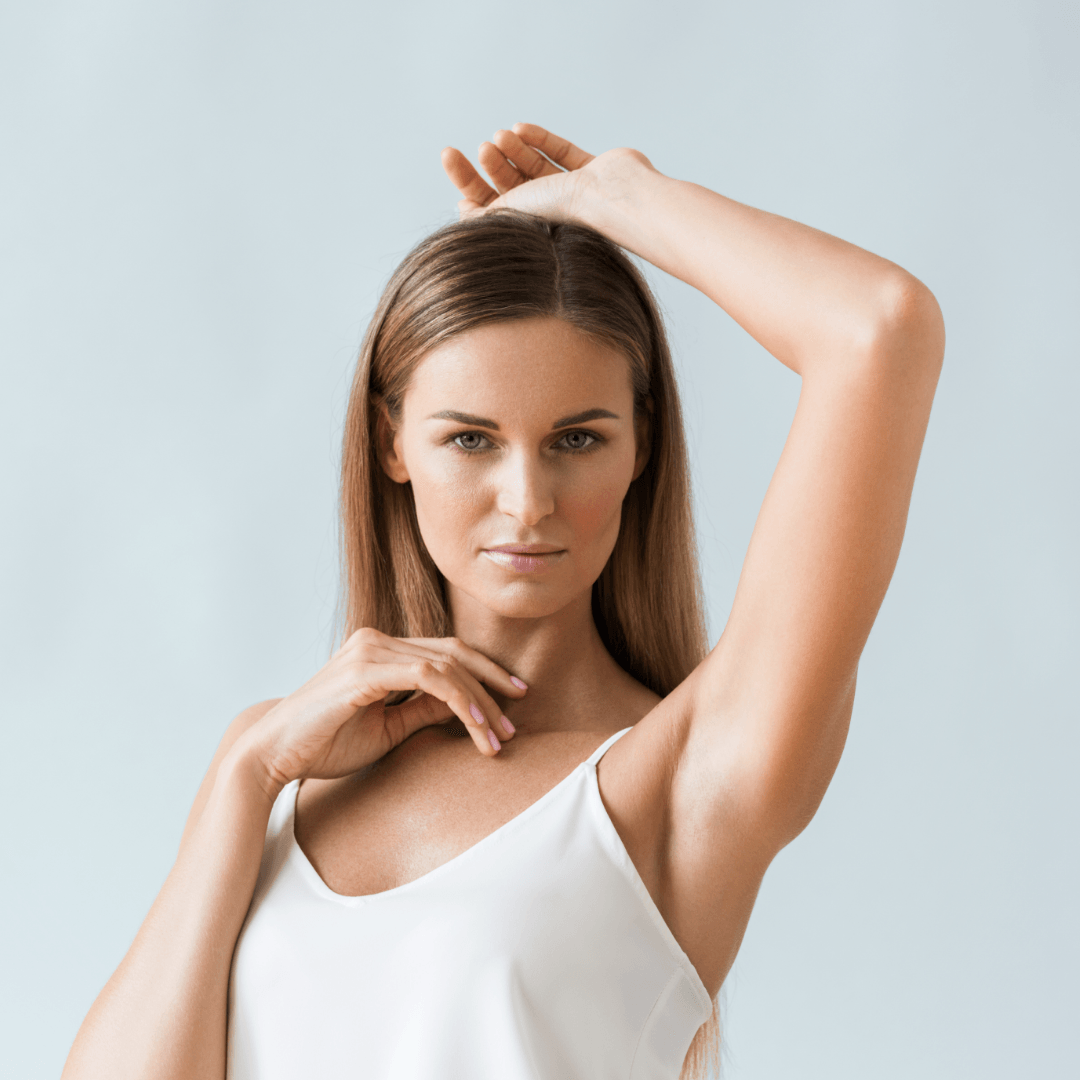
The human body has about 3 million so-called eccrine sweat glands, which are responsible for temperature regulation and thus protect the body from overheating. They are located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. But how exactly does temperature regulation work? It’s quite simple. The wet sweat that emerges from the pores evaporates on our skin, creating a cooling effect. This is also known as evaporative cooling.
Sweating is therefore a vital process. Even during energy production, when nutrients are burned, so much heat is generated that the body temperature inside the body would actually have to rise by about one degree per hour. Heat, physical exertion, and excitement can further increase body temperature. To prevent all these factors from causing the body to overheat, the body produces sweat – our natural and bodily cooling agent.
However, some people’s sweat glands produce unnecessarily large amounts of this cooling agent. They sweat continuously and extremely heavily, even without being exposed to particular physical exertion, for example. The actual causes and reasons for excessive sweating are diverse and often difficult to identify.
Excessive sweating from unknown causes
For reasons not yet clarified, some people’s sweat glands produce sweat more frequently than is actually necessary for temperature regulation and energy production. It is suspected that an overfunction of the sweat glands or an overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls sweat gland production, is the underlying cause. Those affected often sweat in attacks and up to several times a day. The sweating attacks are usually limited to certain body regions, such as the armpits, soles of the feet, back, scalp, or forehead. For some people, even slight stimuli are enough to make the body start sweating. For others, sweating occurs suddenly and without a prior trigger. The intensity of sweating also varies significantly: the disorder ranges from beads of sweat on the forehead and dark sweat stains under the armpits to actual streams of sweat. Those affected are usually only troubled by the unpleasant sweating attacks during the day. At night, however, they often have no complaints.
Stress as a trigger for excessive sweating
Stress and emotional strain are considered one of the main causes of excessive sweating. In a milder form, almost everyone knows this phenomenon: when you are tense, excited, or nervous, the body can start to sweat. Damp, shaky hands and a few small beads of sweat at the hairline are a completely normal reaction of the body to a stressful situation.
If someone is under constant pressure, this can also affect sweating. Many people who are under chronic stress complain of sudden sweating attacks, even at night. The psyche plays a decisive role in this context. Chronic stress negatively affects mental well-being and can lead to depressive moods, sleep disorders, and nervousness, among other things. Due to the psychological strain, the body consequently releases more stress hormones, which in turn give the command to produce sweat.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause
In addition, hormonally induced changes can also be a reason for increased sweating. During pregnancy or menopause, excessive sweating is therefore not uncommon. Especially during menopause, many women complain of sudden sweating attacks and increased sweating. It is assumed that the cause lies in the declining estrogen levels. This disrupts the hormonal balance and the body’s temperature regulation works inaccurately: the brain sends a cooling signal even though it is not actually necessary.
Excessive sweating can also occur during pregnancy. Here too, hormonal changes in the body play a decisive role. The female body now has to supply not just one person but two sufficiently with nutrients. The result: the blood circulation is stimulated and body temperature rises. To compensate for the temperature increase and protect the body from overheating, sweat production is increased. Those who feel uncomfortable can counteract this with light clothing made of natural fibers and a conscious, balanced diet – but fundamentally, this is a completely normal bodily reaction.
Unhealthy lifestyle
Besides the causes just mentioned, lifestyle often plays a major role. To counteract excessive sweating, one should first take a close look at their own lifestyle. Do I move enough? Do I exercise? Do I eat healthily? Do I have too much stress? All these are factors that can influence sweat production. Often, it is spicy foods, too much coffee, or alcohol that rev up sweat production. Overweight is also a common cause because the extra pounds make even small movements difficult, so the body reacts even to minor exertion. However, if someone sweats excessively despite a healthy lifestyle or notices a change, they can seek advice from a general practitioner or dermatologist.